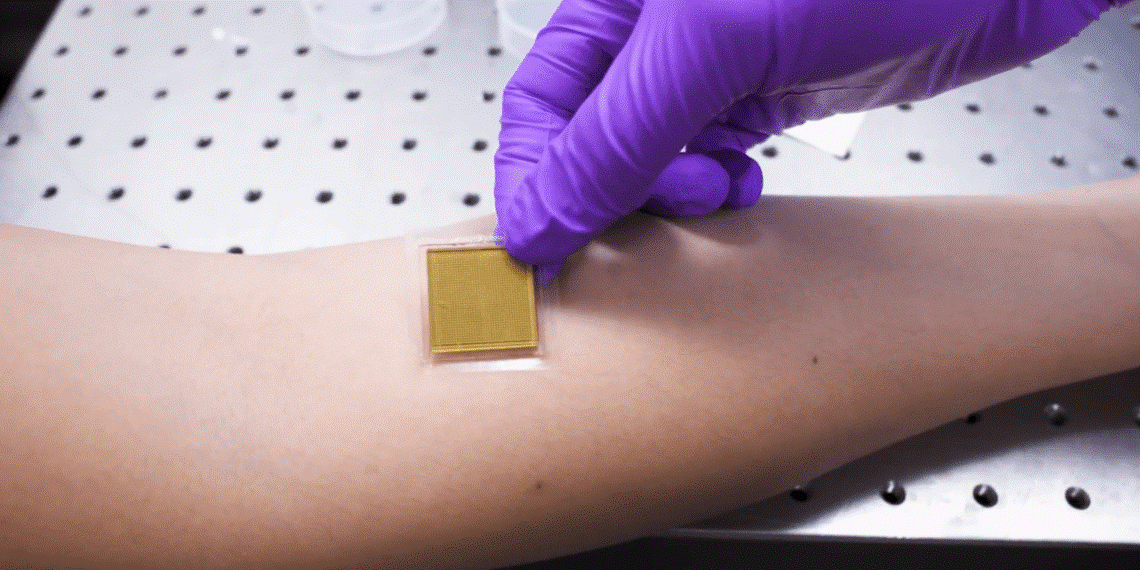
New stamp-sized ultrasound adhesives deliver clear images of the heart, lungs, and other internal organs.
Abstract
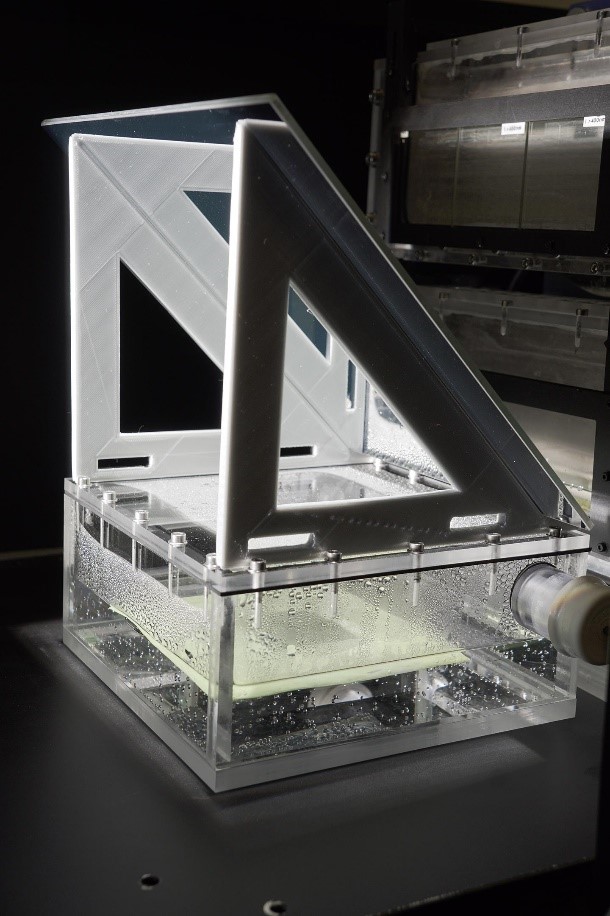
Continuous imaging of internal organs over days could provide crucial information about health and diseases and enable insights into developmental biology. We report a bioadhesive ultrasound (BAUS) device that consists of a thin and rigid ultrasound probe robustly adhered to the skin via a couplant made of a soft, tough, antidehydrating, and bioadhesive hydrogel-elastomer hybrid. The BAUS device provides 48 hours of continuous imaging of diverse internal organs, including blood vessels, muscle, heart, gastrointestinal tract, diaphragm, and lung. The BAUS device could enable diagnostic and monitoring tools for various diseases.
Read More
Floating “Artificial Leaves” Generate Clean Fuels From Sunlight and Water
Scientists have developed floating ‘artificial leaves’ that generate clean fuels from sunlight and water. They could eventually operate on a large scale at sea.
Abstract
Floating perovskite-BiVO4 devices for scalable solar fuel production
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) artificial leaves hold the potential to lower the costs of sustainable solar fuel production by integrating light harvesting and catalysis within one compact device. However, current deposition techniques limit their scalability1, whereas fragile and heavy bulk materials can affect their transport and deployment. Here we demonstrate the fabrication of lightweight artificial leaves by employing thin, flexible substrates and carbonaceous protection layers. Lead halide perovskite photocathodes deposited onto indium tin oxide-coated polyethylene terephthalate achieved an activity of 4,266 µmol H2 g−1 h−1 using a platinum catalyst, whereas photocathodes with a molecular Co catalyst for CO2 reduction attained a high CO:H2 selectivity of 7.2 under lower (0.1 sun) irradiation. The corresponding lightweight perovskite-BiVO4 PEC devices showed unassisted solar-to-fuel efficiencies of 0.58% (H2) and 0.053% (CO), respectively. Their potential for scalability is demonstrated by 100 cm2 stand-alone artificial leaves, which sustained a comparable performance and stability (of approximately 24 h) to their 1.7 cm2 counterparts. Bubbles formed under operation further enabled 30–100 mg cm−2 devices to float, while lightweight reactors facilitated gas collection during outdoor testing on a river. This leaf-like PEC device bridges the gulf in weight between traditional solar fuel approaches, showcasing activities per gram comparable to those of photocatalytic suspensions and plant leaves. The presented lightweight, floating systems may enable open-water applications, thus avoiding competition with land use.
Read More
Predicting Others’ Behavior on the Road With Artificial Intelligence
M2I: From Factored Marginal Trajectory Prediction to Interactive Prediction
Abstract
Predicting future motions of road participants is an important task for driving autonomously in urban scenes. Existing models excel at predicting marginal trajectories for single agents, yet it remains an open question to jointly predict scene compliant trajectories over multiple agents. The challenge is due to exponentially increasing prediction space as a function of the number of agents. In this work, we exploit the underlying relations between interacting agents and decouple the joint prediction problem into marginal prediction problems. Our proposed approach M2I first classifies interacting agents as pairs of influencers and reactors, and then leverages a marginal prediction model and a conditional prediction model to predict trajectories for the influencers and reactors, respectively. The predictions from interacting agents are combined and selected according to their joint likelihoods. Experiments show that our simple but effective approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Waymo Open Motion Dataset interactive prediction benchmark.
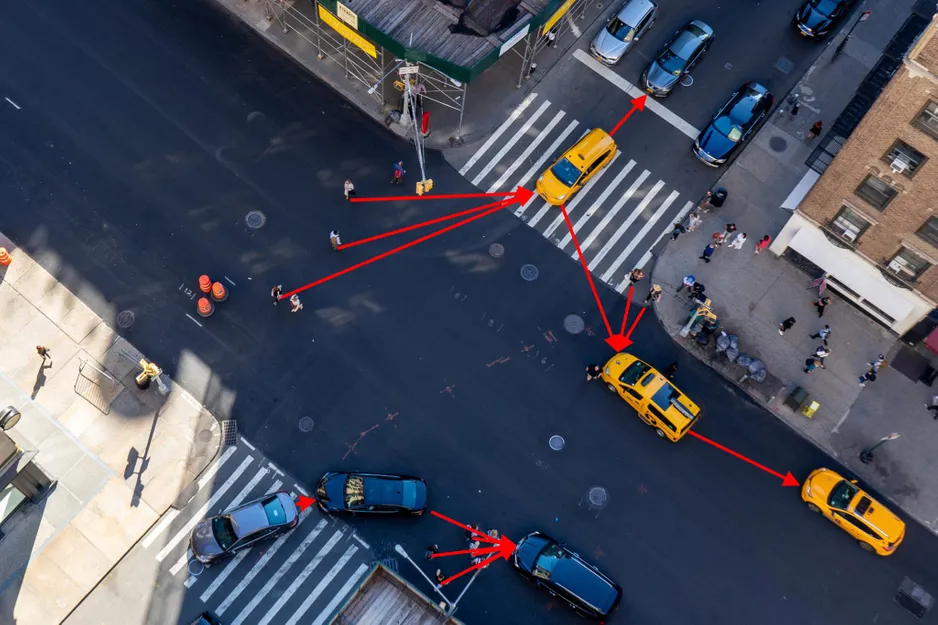

Researchers have created a machine-learning system that efficiently predicts the future trajectories of multiple road users, like drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians, which could enable an autonomous vehicle to more safely navigate city streets. If a robot is going to navigate a vehicle safely through downtown Boston, it must be able to predict what nearby drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians are going to do next. Credit: MIT
Summary:
Portable Seawater Desalination System for Generating Drinkable Water in Remote Locations.
Summary:
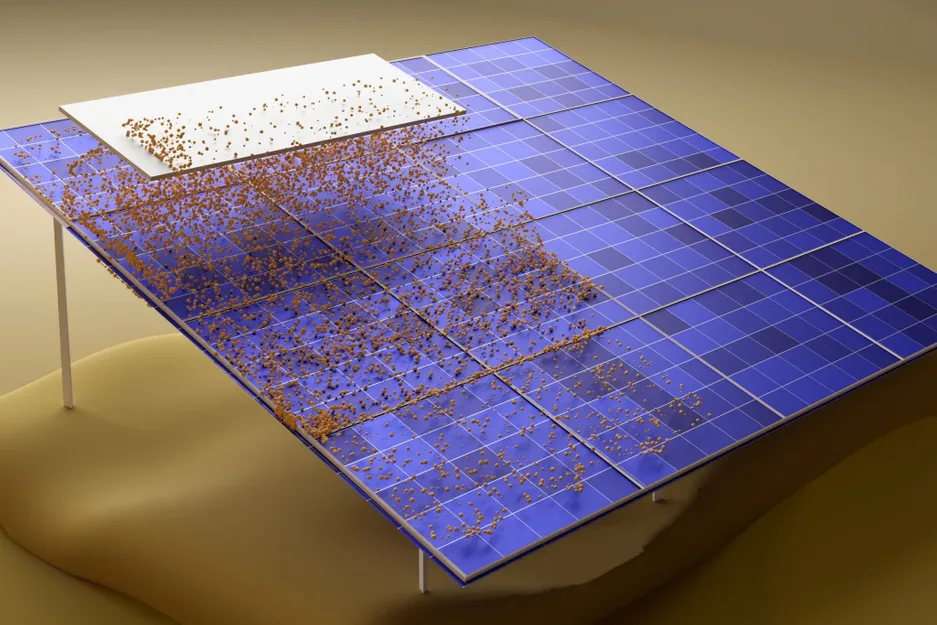
Electrostatic dust removal using adsorbed moisture–assisted charge induction for sustainable operation of solar panels.
Summary:
New technology that could store heat for days or even months, helping the shift towards net zero, is the focus of a new project involving the Active Building Centre Research Programme, led by Swansea University, which has just been awarded funding of £146,000.
Summary:
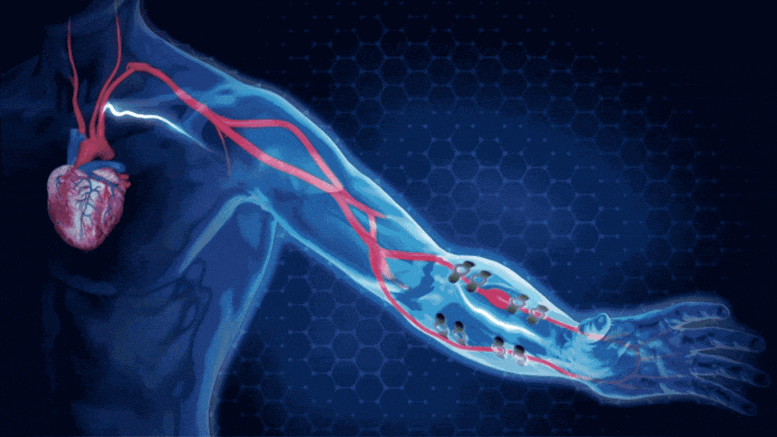
Continuous monitoring of arterial blood pressure (BP) in non-clinical (ambulatory) settings is essential for understanding numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases. Besides their importance in medical diagnosis, ambulatory BP monitoring platforms can advance disease correlation with individual behaviour, daily habits and lifestyle, potentially enabling analysis of root causes, prognosis and disease prevention. Although conventional ambulatory BP devices exist, they are uncomfortable, bulky and intrusive.
Summary:
Cement is a binder, a substance used in construction that hardens, sets, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. When sand and gravel are combined with cement, concrete is produced. Cement is classified as hydraulic or non-hydraulic, with non-hydraulic cement not setting when water is present, while hydraulic cement needs a chemical reaction between dry materials and water.
Summary:
A nanomaterials-engineered penetrating sealer developed by Washington State University researchers is able to better protect concrete from moisture and salt – the two most damaging factors in crumbling concrete infrastructure in northern states.
Summary:
Existing approaches for embedding unobtrusive tags inside 3D obgaps inside for the tag’s bits, which appear at a diferent intensity in the infrared image.
Summary:
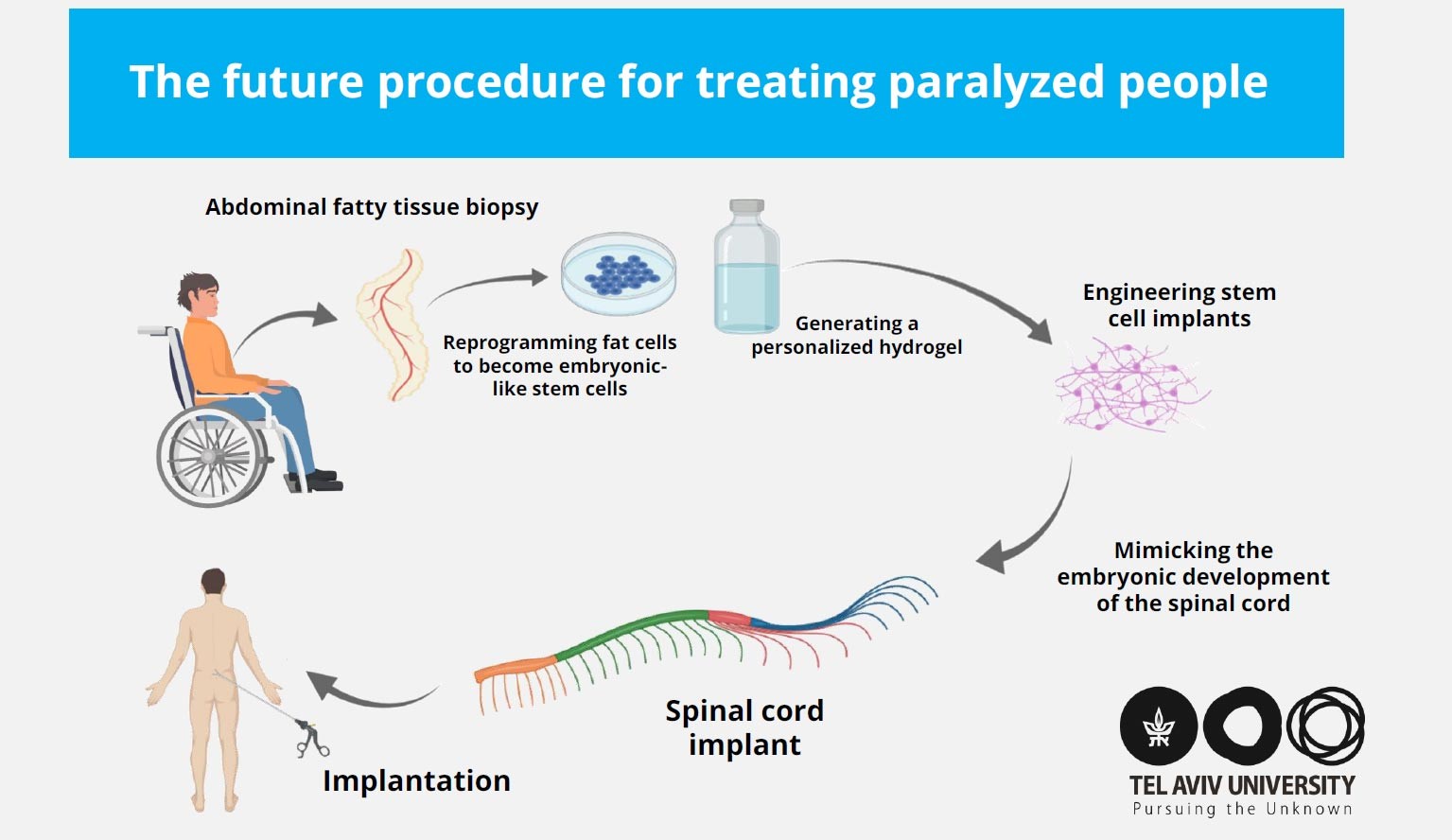
Cell therapy using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons is considered a promising approach to regenerate the injured spinal cord (SC). However, the scar formed at the chronic phase is not a permissive microenvironment for cell or biomaterial engraftment or for tissue assembly.
Summary:
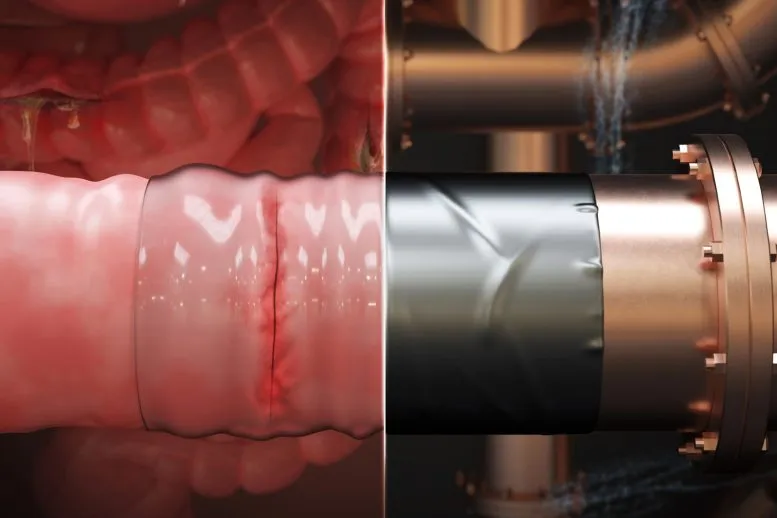
A new MIT-designed surgical sticky tape can be applied quickly and easily, like duct tape to a pipe, to repair leaks and tears in the gastrointestinal tract and other tissues and organs. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
Summary:
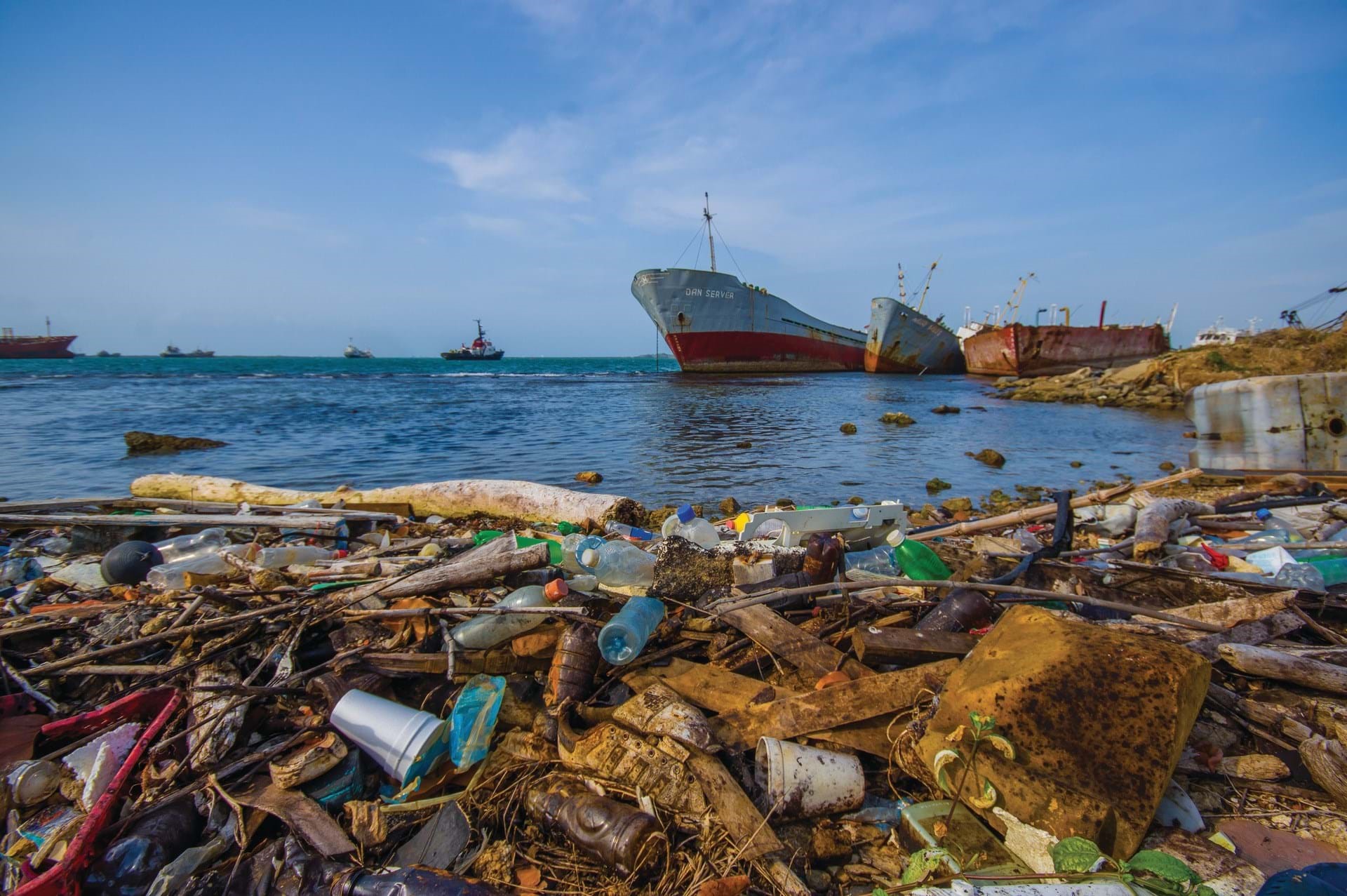
Clearing up marine plastic pollution is energy intensive – but ships could convert the plastic they collect into fuel and create a self-sustaining clean-up operation...
Summary:
LoRaWAN is a wireless technology for Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN). Today, it is considered as one of the most serious alternatives for IoT thanks to its low cost, low power consumption equipments and its open business model...
Summary:
Meta and Microsoft's new virtual reality projects have been met with suspicion by many, but history has shown that people are often right to be wary of technological change...
Summary:
Wireless communications is the transferring of information between two or more points which are not physically connected. Distances can be short, which is used for television....
Summary:
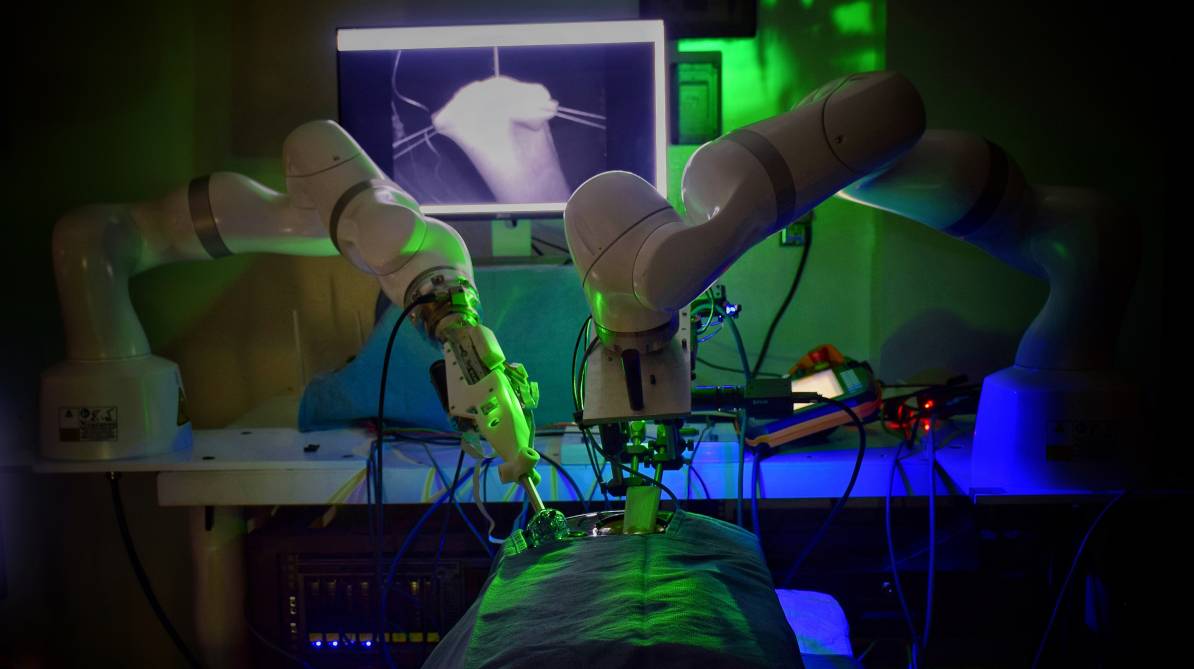
A robot has performed laparoscopic surgery on the soft tissue of a pig without the guiding hand of a human -- a significant step in robotics toward fully automated surgery on humans.
Summary:
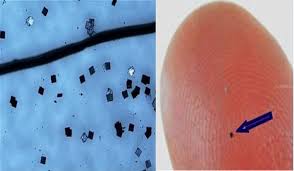
Researchers have used a unique tool inserted into an electron microscope to create a transistor that's 25,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
Measurements of trees’ impact on 5G transmissions could prove vital to using a new class of signal.
Summary:
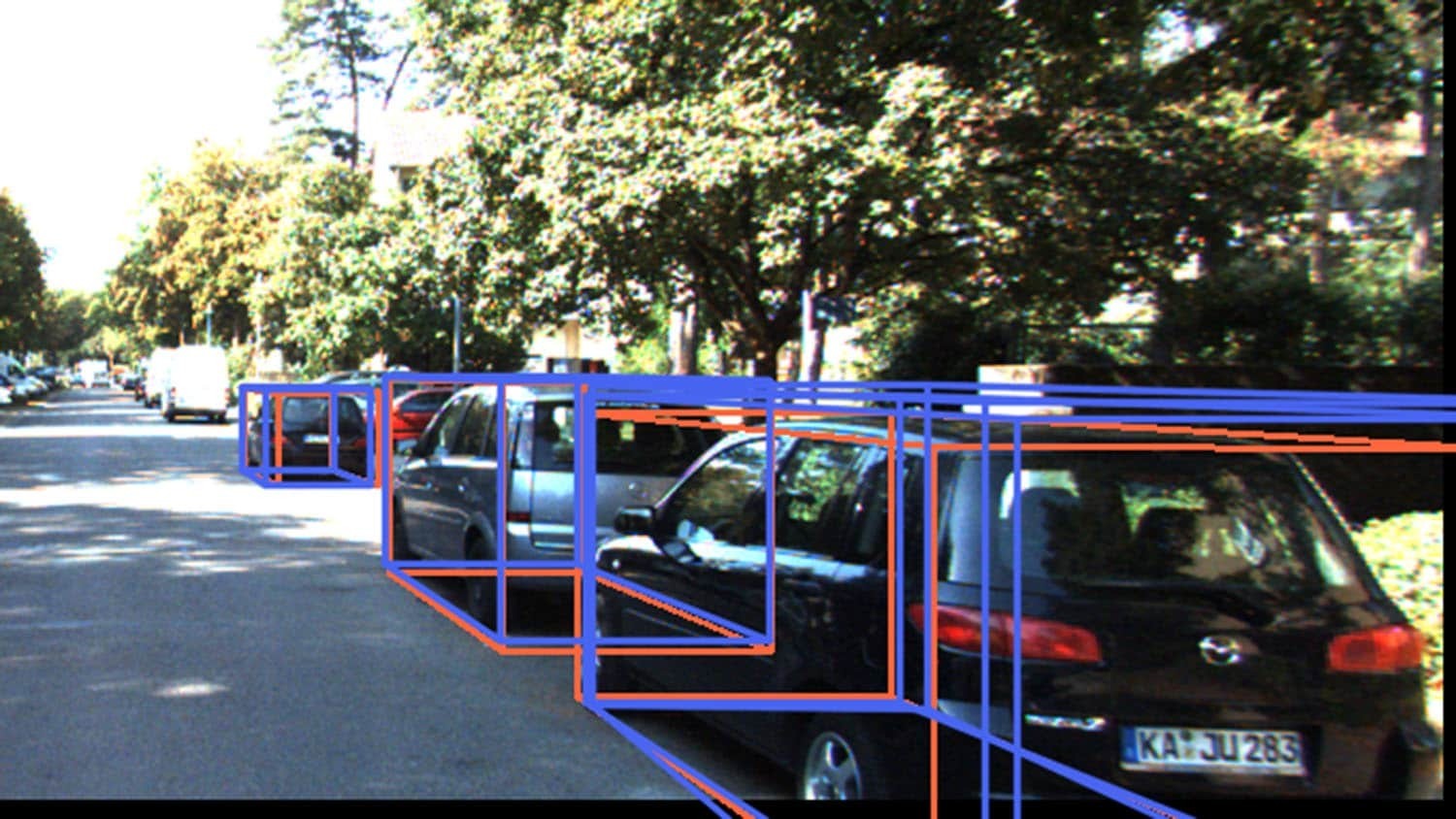
Researchers have developed a new technique, called MonoCon, that improves the ability of artificial intelligence (AI) programs to identify three-dimensional (3D) objects, and how those objects relate to each other in space, using two-dimensional (2D) images.
The massive benefits of 4G technology is already experienced by the todays community and the technological innovations are ready to bring the more sophisticated and wonderful experience in communication technology in the name of 5G technology.